For US Healthcare Professionals
I am a:
For US Healthcare Professionals
Full Prescribing InformationIN PATIENTS WITH AN INADEQUATE RESPONSE* TO STELARA®
TREMFYA® demonstrated significant skin clearance1
NAVIGATE: Major secondary endpoint at Week 28 (12 weeks after randomization)†
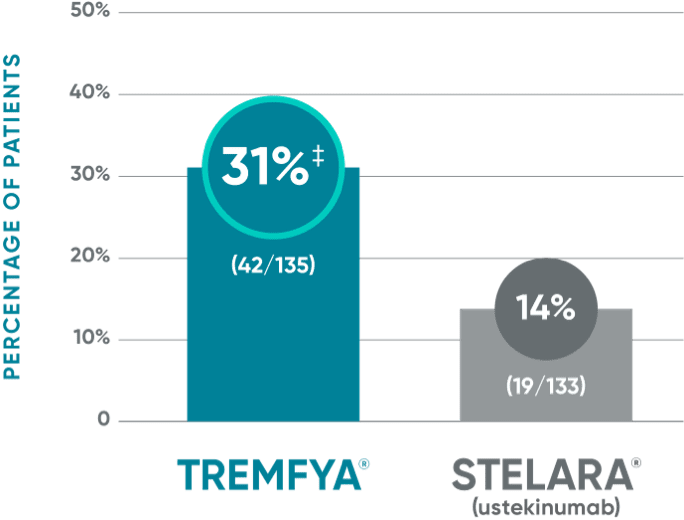
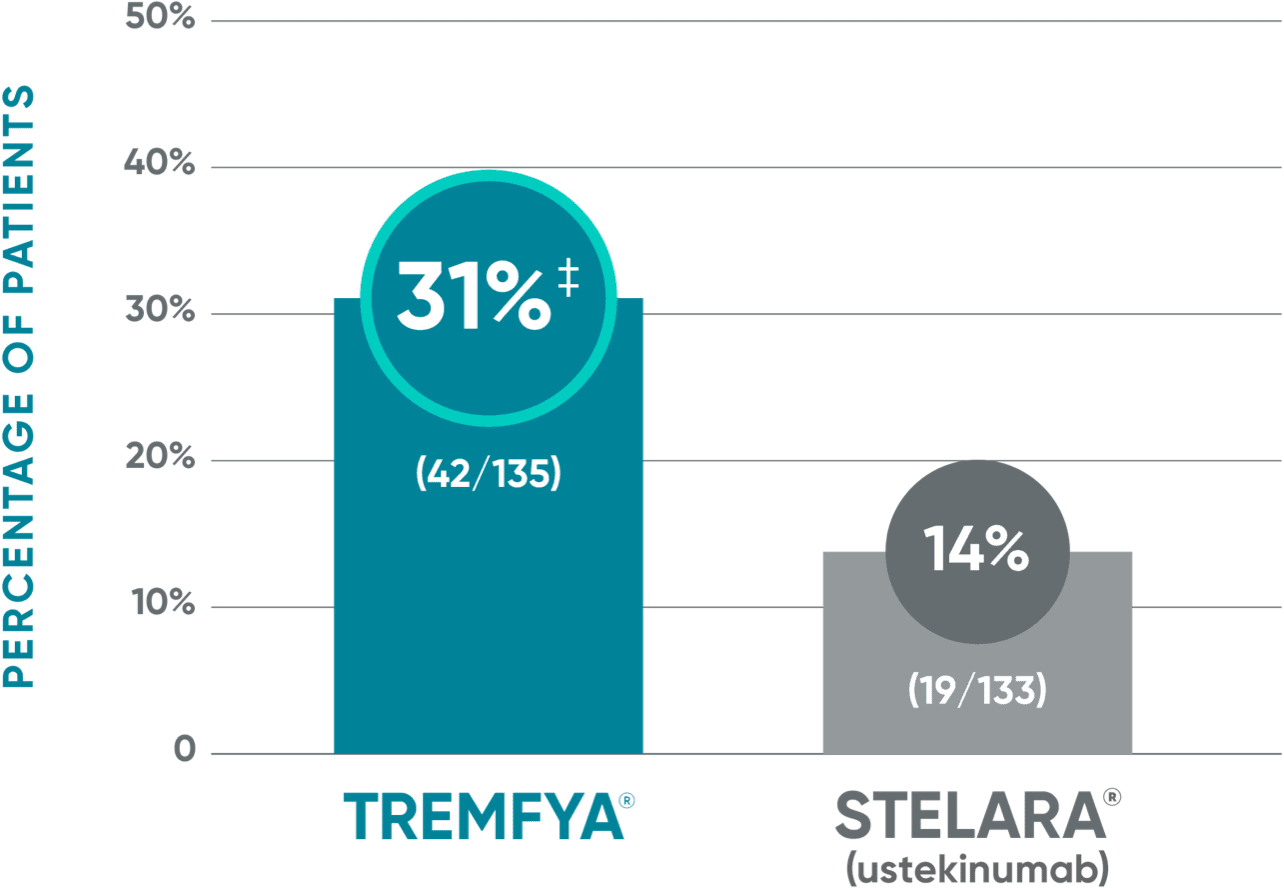
‡P<0.001 vs STELARA®.
VOYAGE co-primary endpoints at Week 16 (NRI)2,3:
VOYAGE 1—PASI 90: TREMFYA® 73% (241/329), placebo 3% (5/174) (P<0.001). IGA 0/1: TREMFYA® 85% (280/329), placebo 7% (12/174) (P<0.001). VOYAGE 2—PASI 90: TREMFYA® 70% (347/496), placebo 2% (6/248) (P<0.001). IGA 0/1: TREMFYA® 84% (417/496), placebo 8% (21/248) (P<0.001).
Psoriasis Symptoms and Signs Diary (Week 16): Greater improvements in symptoms of psoriasis (itch, pain, stinging, burning, and skin tightness).2
*IGA ≥2 at Week 16 after initial treatment with US-licensed STELARA® (dosed 45 mg or 90 mg according to the patient's baseline weight at Week 0 or Week 4).
†More than twice as many patients treated with TREMFYA® achieved IGA 0/1 (with a ≥2-grade improvement) at Week 28.
View STELARA® Indication, Important Safety Information and full Prescribing Information.
References: 1. Langley RG, Tsai, TF, Flavin S, et al. Efficacy and safety of guselkumab in patients with psoriasis who have an inadequate response to ustekinumab: results of the randomized, double-blind, phase III NAVIGATE trial. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178(1):114-123. 2. TREMFYA® (guselkumab) [Prescribing Information]. Horsham, PA: Janssen Biotech, Inc. 3. Data on file. Janssen Biotech, Inc.
IN PATIENTS WITH AN INADEQUATE RESPONSE* TO STELARA®
PASI 90 response rate from Week 16 through Week 521
NAVIGATE: Prespecified exploratory endpoint from Week 16 to Week 52†


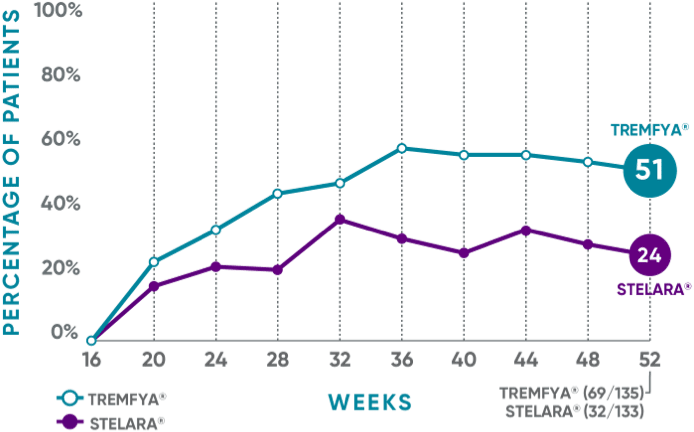
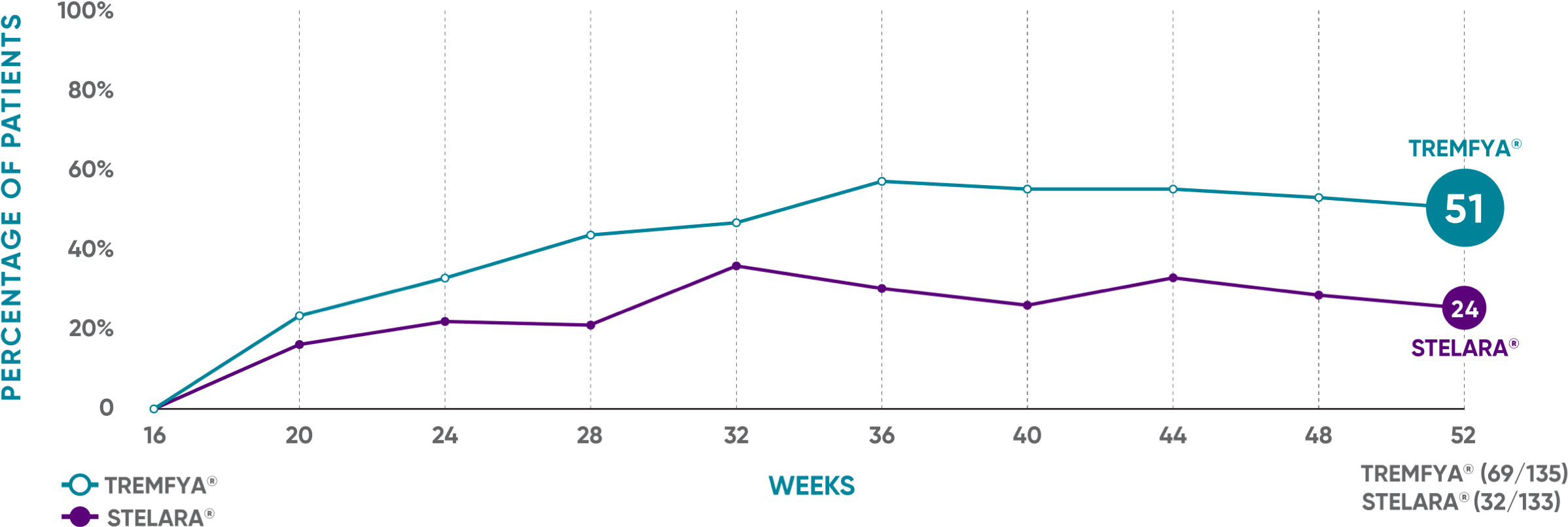
The same patients may not have responded at each time point.
†The proportion of patients who achieved PASI 90 from Week 16 through Week 52 was a prespecified exploratory endpoint that was not adjusted for multiplicity; P values were considered nominal.
VOYAGE co-primary endpoints at Week 16 (NRI)2,3:
VOYAGE 1—PASI 90: TREMFYA® 73% (241/329), placebo 3% (5/174) (P<0.001). IGA 0/1: TREMFYA® 85% (280/329), placebo 7% (12/174) (P<0.001). VOYAGE 2—PASI 90: TREMFYA® 70% (347/496), placebo 2% (6/248) (P<0.001). IGA 0/1: TREMFYA® 84% (417/496), placebo 8% (21/248) (P<0.001).
Psoriasis Symptoms and Signs Diary (Week 16): Greater improvements in symptoms of psoriasis (itch, pain, stinging, burning, and skin tightness).2
*IGA ≥2 at Week 16 after initial treatment with US-licensed STELARA® (dosed 45 mg or 90 mg according to the patient's baseline weight at Week 0 or Week 4).
PASI=Psoriasis Area and Severity Index.
View STELARA® Indication, Important Safety Information and full Prescribing Information.
References: 1. Langley RG, Tsai, TF, Flavin S, et al. Efficacy and safety of guselkumab in patients with psoriasis who have an inadequate response to ustekinumab: results of the randomized, double-blind, phase III NAVIGATE trial. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178(1):114-123. 2. TREMFYA® (guselkumab) [Prescribing Information]. Horsham, PA: Janssen Biotech, Inc. 3. Data on file. Janssen Biotech, Inc.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
STELARA® (ustekinumab) is contraindicated in patients with clinically significant hypersensitivity to ustekinumab or to any of the excipients.
Infections
STELARA® may increase the risk of infections and reactivation of latent infections. Serious bacterial, mycobacterial, fungal, and viral infections requiring hospitalization or otherwise clinically significant infections were reported. In patients with psoriasis, these included diverticulitis, cellulitis, pneumonia, appendicitis, cholecystitis, sepsis, osteomyelitis, viral infections, gastroenteritis, and urinary tract infections. In patients with psoriatic arthritis, this included cholecystitis. In patients with Crohn’s disease, these included anal abscess, gastroenteritis, ophthalmic herpes zoster, pneumonia, and Listeria meningitis. In patients with ulcerative colitis, these included gastroenteritis, ophthalmic herpes zoster, pneumonia, and listeriosis.
Treatment with STELARA® should not be initiated in patients with a clinically important active infection until the infection resolves or is adequately treated. Consider the risks and benefits of treatment prior to initiating use of STELARA® in patients with a chronic infection or a history of recurrent infection. Instruct patients to seek medical advice if signs or symptoms suggestive of an infection occur while on treatment with STELARA® and consider discontinuing STELARA® for serious or clinically significant infections until the infection resolves or is adequately treated.
Theoretical Risk for Vulnerability to Particular Infections
Individuals genetically deficient in IL-12/IL-23 are particularly vulnerable to disseminated infections from mycobacteria, Salmonella, and Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccinations. Serious infections and fatal outcomes have been reported in such patients. It is not known whether patients with pharmacologic blockade of IL-12/IL-23 from treatment with STELARA® may be susceptible to these types of infections. Appropriate diagnostic testing should be considered (eg, tissue culture, stool culture) as dictated by clinical circumstances.
Pre-Treatment Evaluation of Tuberculosis (TB)
Evaluate patients for TB prior to initiating treatment with STELARA®. Do not administer STELARA® to patients with active tuberculosis infection. Initiate treatment of latent TB before administering STELARA®. Closely monitor patients receiving STELARA® for signs and symptoms of active TB during and after treatment.
Malignancies
STELARA® is an immunosuppressant and may increase the risk of malignancy. Malignancies were reported among patients who received STELARA® in clinical studies. The safety of STELARA® has not been evaluated in patients who have a history of malignancy or who have a known malignancy. There have been reports of the rapid appearance of multiple cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas in patients receiving STELARA® who had risk factors for developing non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC). All patients receiving STELARA®, especially those >60 years or those with a history of PUVA or prolonged immunosuppressant treatment, should be monitored for the appearance of NMSC.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and angioedema, have been reported with STELARA®. If an anaphylactic or other clinically significant hypersensitivity reaction occurs, institute appropriate therapy and discontinue STELARA®.
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES)
Two cases of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES), also known as Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS), were reported in clinical trials. Cases have also been reported in postmarketing experience in patients with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and Crohn’s disease. Clinical presentation included headaches, seizures, confusion, visual disturbances, and imaging changes consistent with PRES a few days to several months after ustekinumab initiation. A few cases reported latency of a year or longer. Patients recovered with supportive care following withdrawal of ustekinumab.
Monitor all patients treated with STELARA® for signs and symptoms of PRES. If PRES is suspected, promptly administer appropriate treatment and discontinue STELARA®.
Immunizations
Prior to initiating therapy with STELARA®, patients should receive all age-appropriate immunizations recommended by current guidelines. Patients being treated with STELARA® should not receive live vaccines. BCG vaccines should not be given during treatment or within one year of initiating or discontinuing STELARA®. Exercise caution when administering live vaccines to household contacts of STELARA® patients, as shedding and subsequent transmission to STELARA® patients may occur. Non-live vaccinations received during a course of STELARA® may not elicit an immune response sufficient to prevent disease.
Concomitant Therapies
The safety of STELARA® in combination with other biologic immunosuppressive agents or phototherapy was not evaluated in clinical studies of psoriasis. Ultraviolet-induced skin cancers developed earlier and more frequently in mice. In psoriasis studies, the relevance of findings in mouse models for malignancy risk in humans is unknown. In psoriatic arthritis studies, concomitant methotrexate use did not appear to influence the safety or efficacy of STELARA®. In Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis induction studies, concomitant use of 6-mercaptopurine, azathioprine, methotrexate, and corticosteroids did not appear to influence the overall safety or efficacy of STELARA®.
Noninfectious Pneumonia
Cases of interstitial pneumonia, eosinophilic pneumonia, and cryptogenic organizing pneumonia have been reported during post-approval use of STELARA®. Clinical presentations included cough, dyspnea, and interstitial infiltrates following one to three doses. Serious outcomes have included respiratory failure and prolonged hospitalization. Patients improved with discontinuation of therapy and, in certain cases, administration of corticosteroids. If diagnosis is confirmed, discontinue STELARA® and institute appropriate treatment.
Allergen Immunotherapy
STELARA® may decrease the protective effect of allergen immunotherapy (decrease tolerance) which may increase the risk of an allergic reaction to a dose of allergen immunotherapy. Therefore, caution should be exercised in patients receiving or who have received allergen immunotherapy, particularly for anaphylaxis.
Most Common Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions (≥3% and higher than that with placebo) in adults from psoriasis clinical studies for STELARA® 45 mg, STELARA® 90 mg, or placebo were: nasopharyngitis (8%, 7%, 8%), upper respiratory tract infection (5%, 4%, 5%), headache (5%, 5%, 3%), and fatigue (3%, 3%, 2%), respectively. The safety profile in pediatric patients with plaque psoriasis was similar to that of adults with plaque psoriasis. In psoriatic arthritis (PsA) studies, a higher incidence of arthralgia and nausea was observed in patients treated with STELARA® when compared with placebo (3% vs 1% for both). In Crohn’s disease induction studies, common adverse reactions (3% or more of patients treated with STELARA® and higher than placebo) reported through Week 8 for STELARA® 6 mg/kg intravenous single infusion or placebo included: vomiting (4% vs 3%). In the Crohn’s disease maintenance study, common adverse reactions (3% or more of patients treated with STELARA® and higher than placebo) reported through Week 44 for STELARA® 90 mg subcutaneous injection or placebo were: nasopharyngitis (11% vs 8%), injection site erythema (5% vs 0%), vulvovaginal candidiasis/mycotic infection (5% vs 1%), bronchitis (5% vs 3%), pruritus (4% vs 2%), urinary tract infection (4% vs 2%) and sinusitis (3% vs 2%). In the ulcerative colitis induction study, common adverse reactions (3% or more of patients treated with STELARA® and higher than placebo) reported through Week 8 for STELARA® 6 mg/kg intravenous single infusion or placebo included: nasopharyngitis (7% vs 4%). In the ulcerative colitis maintenance study, common adverse reactions (3% or more of patients treated with STELARA® and higher than placebo) reported through Week 44 for STELARA® 90 mg subcutaneous injection or placebo included: nasopharyngitis (24% vs 20%), headache (10% vs 4%), abdominal pain (7% vs 3%), influenza (6% vs 5%), fever (5% vs 4%), diarrhea (4% vs 1%), sinusitis (4% vs 1%), fatigue (4% vs 2%), and nausea (3% vs 2%).
Please click to see the full Prescribing Information and Medication Guide for STELARA®. Provide the Medication Guide to your patients and encourage discussion.
cp-124933v5
INDICATIONS
STELARA® (ustekinumab) is indicated for the treatment of patients 6 years and older with active psoriatic arthritis.
STELARA® (ustekinumab) is indicated for the treatment of patients 6 years or older with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy.
STELARA® (ustekinumab) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease.
STELARA® (ustekinumab) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis.


