For US Healthcare Professionals
I am a:
Difficult-to-treat patient types: Scalp data
VOYAGE 1: ss-IGA 0/1 and ≥2-grade improvement from baseline1,2*
Major secondary endpoint (Week 16)


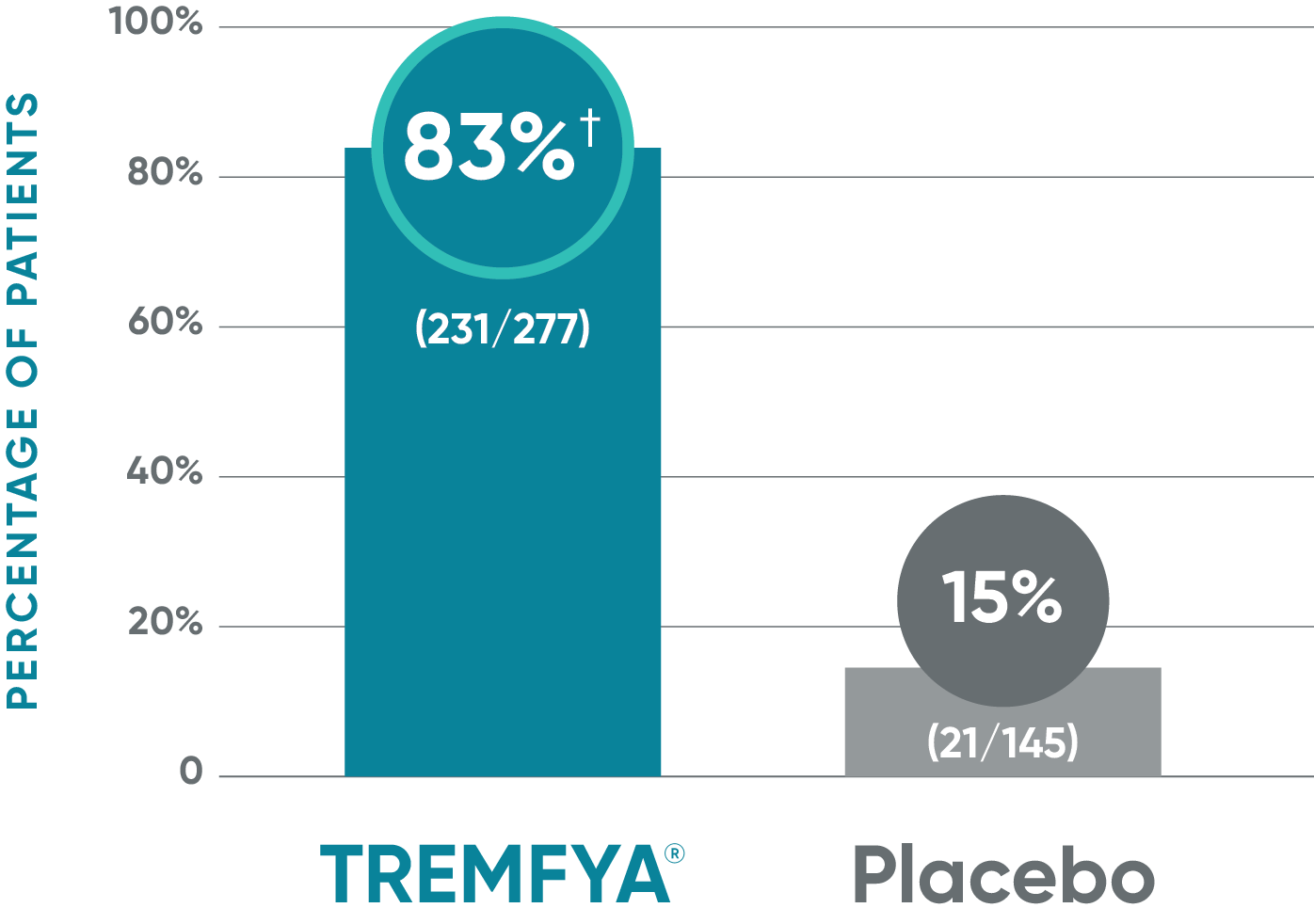
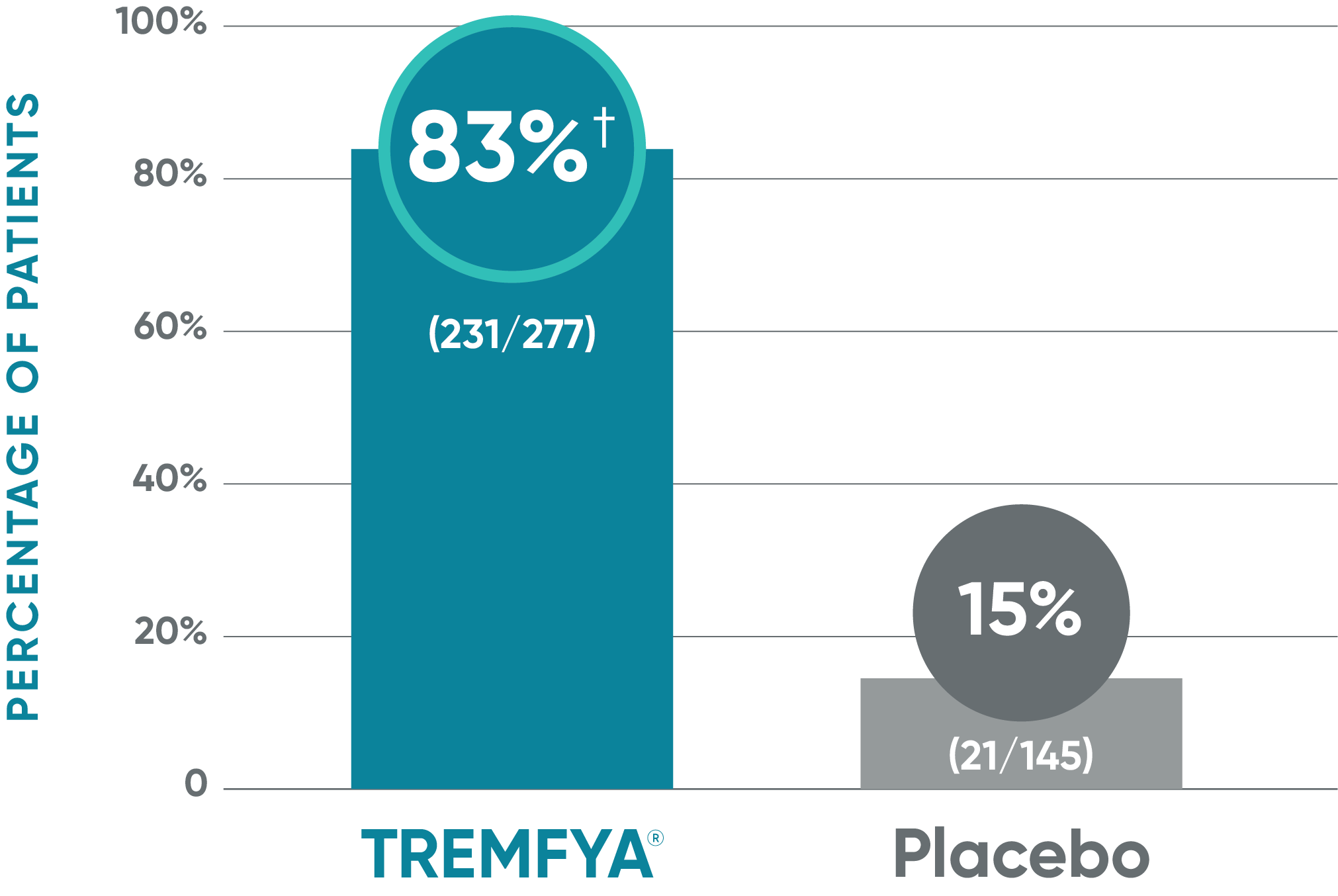
†P<0.001 vs placebo.
*In a subpopulation of patients with ss-IGA score ≥2 at baseline.
‡Prespecified other secondary analysis that was not adjusted for multiplicity; therefore, statistical significance has not been established.
VOYAGE co-primary endpoints at Week 16 (NRI)2,3:
VOYAGE 1—PASI 90: TREMFYA® 73% (241/329), placebo 3% (5/174) (P<0.001). IGA 0/1: TREMFYA® 85% (280/329), placebo 7% (12/174) (P<0.001). VOYAGE 2—PASI 90: TREMFYA® 70% (347/496), placebo 2% (6/248) (P<0.001). IGA 0/1: TREMFYA® 84% (417/496), placebo 8% (21/248) (P<0.001).
Psoriasis Symptoms and Signs Diary (Week 16): Greater improvements in symptoms of psoriasis (itch, pain, stinging, burning, and skin tightness).3
Active comparator at Week 48 not shown.
Nonresponder imputation (NRI) methods were used for analysis.
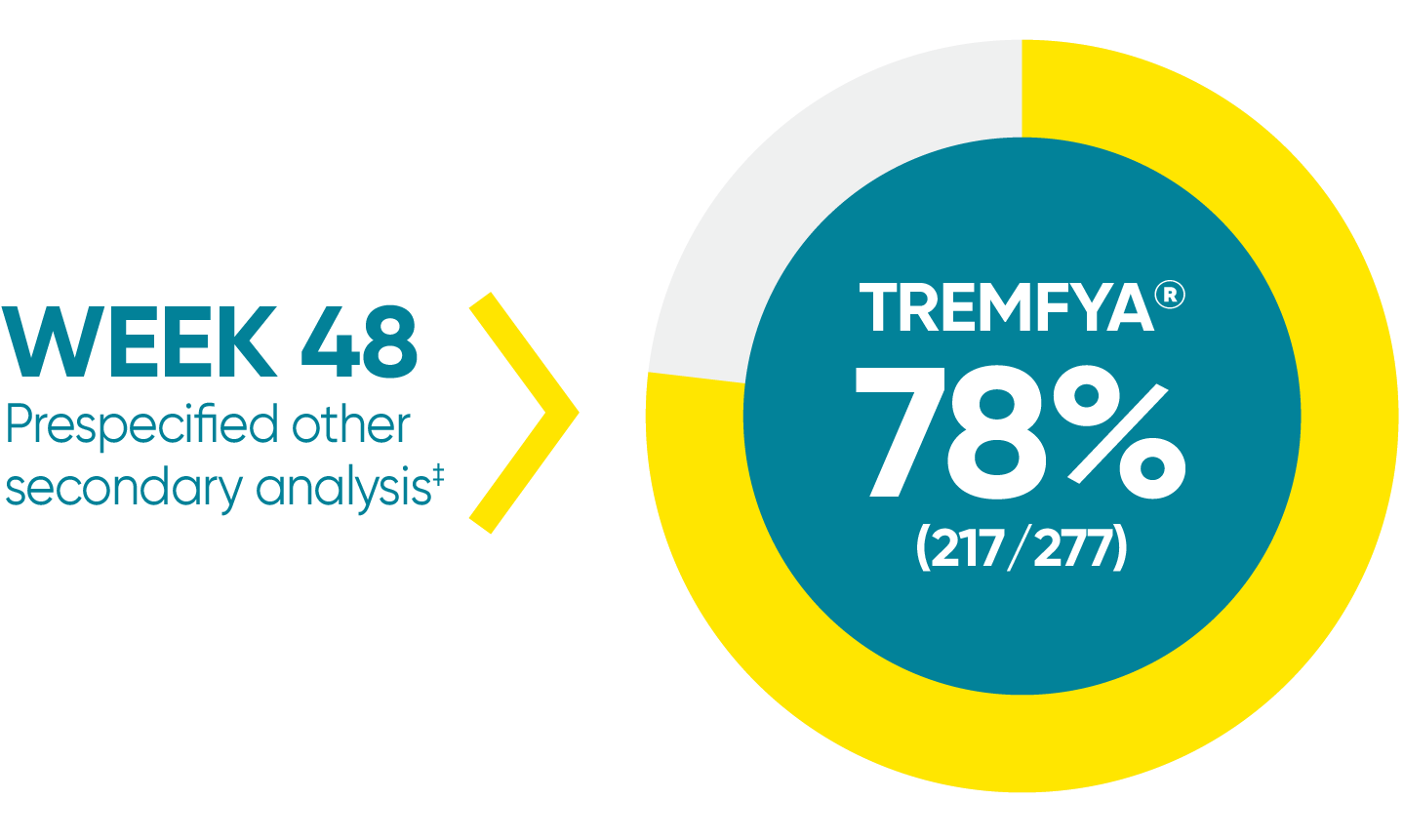
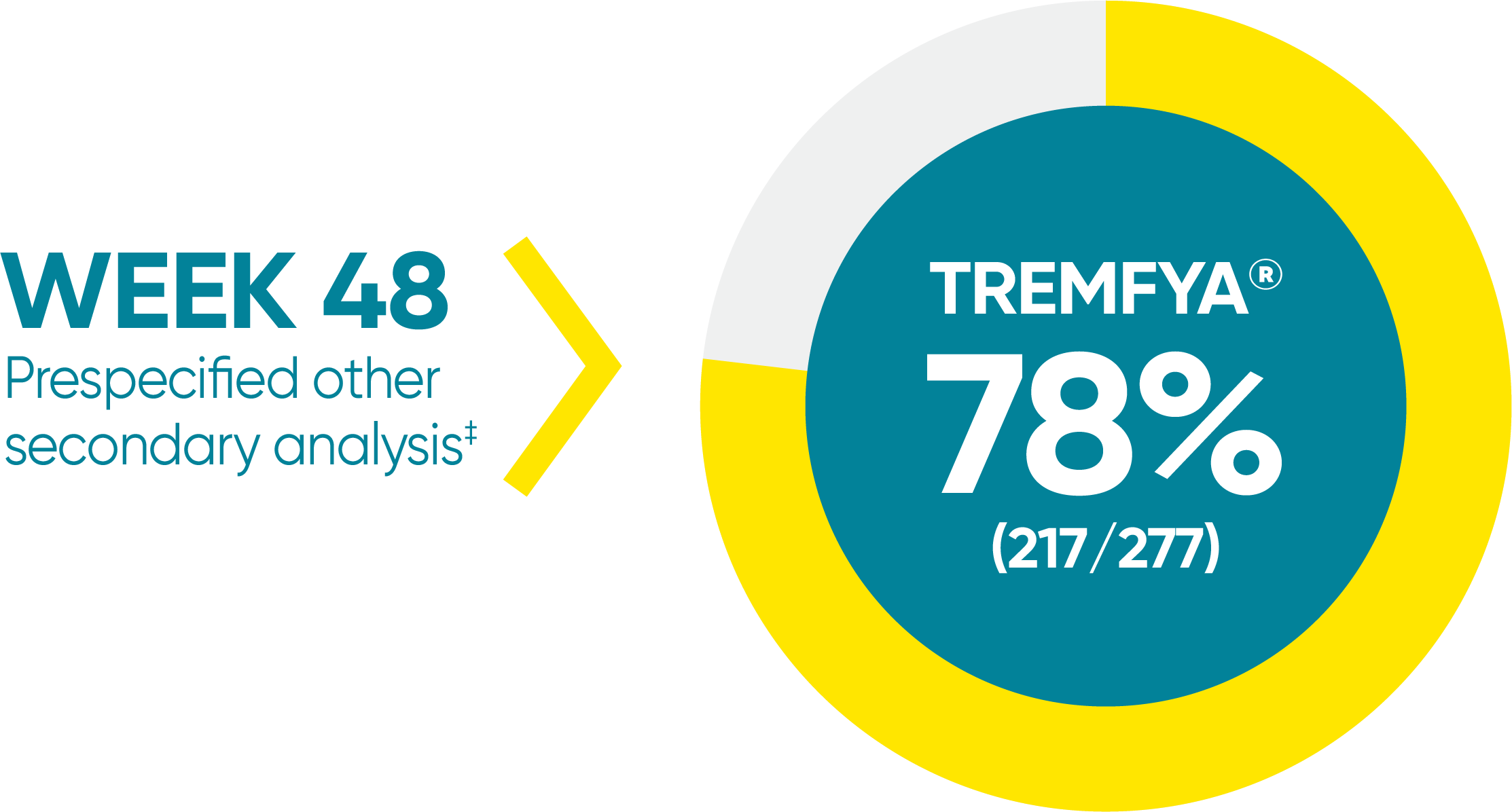
VOYAGE 2: Major secondary endpoint at Week 162,4*
- 81% (329/408) of patients receiving TREMFYA® achieved ss-IGA 0/1 vs 11% (22/202) of patients receiving placebo (P<0.001)
ss-IGA=scalp-specific Investigator's Global Assessment; ss-IGA 0/1=proportion of patients who achieved an ss-IGA score of absence of disease (0) or very mild (1) using a 5-point scale where scalp lesions were assessed in terms of clinical signs of redness, thickness, and scaliness on a scale of 0 to 4: absence of disease (0), very mild (1), mild (2), moderate (3), or severe (4).
References: 1. Blauvelt A, Papp KA, Griffiths CEM, et al. Efficacy and safety of guselkumab, an anti-interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody, compared with adalimumab for the continuous treatment of patients with moderate to severe psoriasis: results from the phase III, double-blinded, placebo- and active comparator-controlled VOYAGE 1 trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76(3):405-417. 2. Data on file. Janssen Biotech, Inc. 3. TREMFYA® (guselkumab) [Prescribing Information]. Horsham, PA: Janssen Biotech, Inc. 4. Reich K, Armstrong AW, Foley P, et al. Efficacy and safety of guselkumab, an anti-interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody, compared with adalimumab for the treatment of patients with moderate to severe psoriasis with randomized withdrawal and retreatment: results from the phase III, double-blind, placebo- and active comparator-controlled VOYAGE 2 trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76(3):418-431.
Difficult-to-treat patient types: Body weight data
VOYAGE 1: PASI 90 response at Week 48 with TREMFYA® by baseline BMI (post hoc analysis)1*
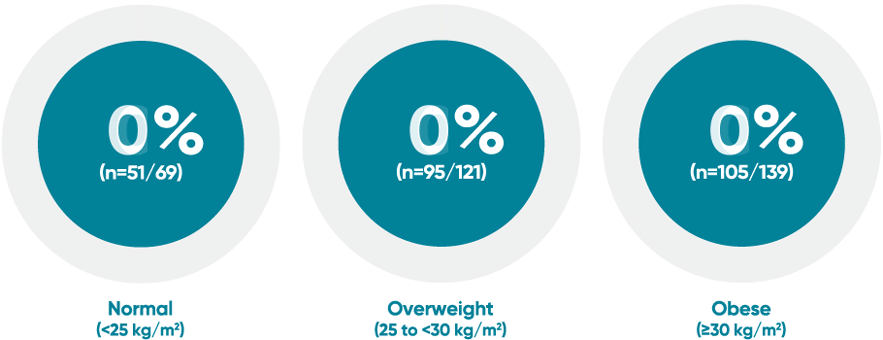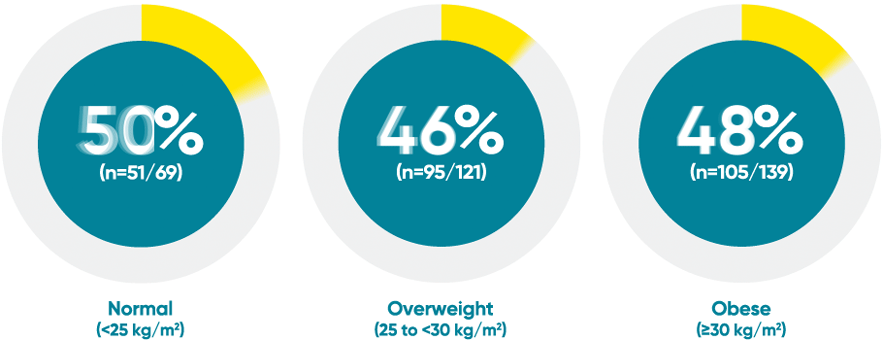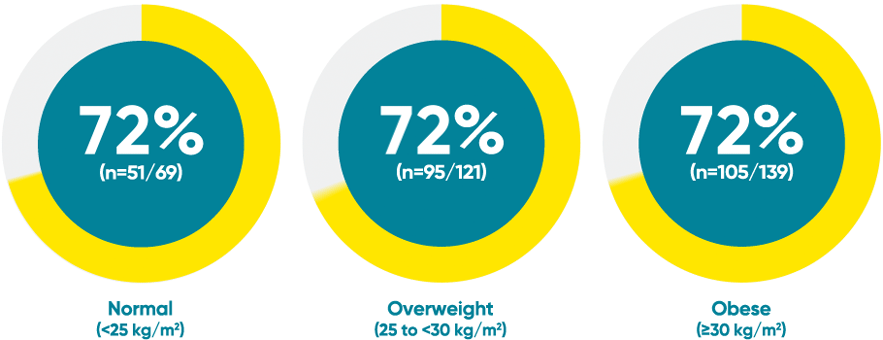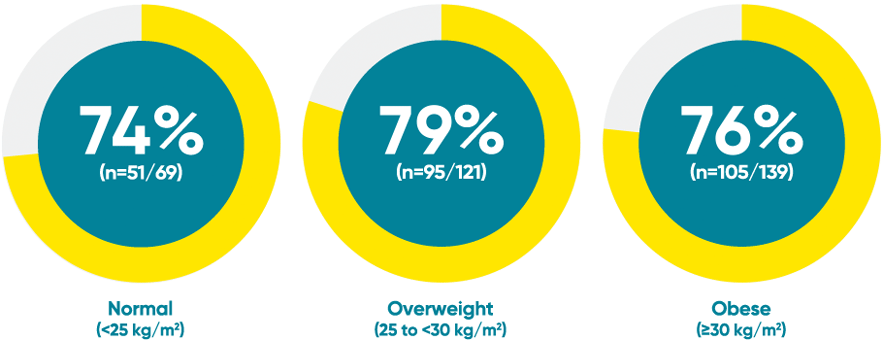
*This is a post hoc analysis; statistical significance has not been established and efficacy comparisons cannot be made.
VOYAGE co-primary endpoints at Week 16 (NRI)1,2:
VOYAGE 1—PASI 90: TREMFYA® 73% (241/329), placebo 3% (5/174) (P<0.001). IGA 0/1: TREMFYA® 85% (280/329), placebo 7% (12/174) (P<0.001). VOYAGE 2—PASI 90: TREMFYA® 70% (347/496), placebo 2% (6/248) (P<0.001). IGA 0/1: TREMFYA® 84% (417/496), placebo 8% (21/248) (P<0.001).
Psoriasis Symptoms and Signs Diary (Week 16): Greater improvements in symptoms of psoriasis (itch, pain, stinging, burning, and skin tightness).2
Active comparator at Week 48 not shown.
Nonresponder imputation (NRI) methods were used for analysis.
BMI=body mass index (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared).
VOYAGE 1: Major secondary endpoint at
Week 481,2
- 73% (84/115) of patients receiving TREMFYA® achieved PASI 90 vs 46% (53/115) of patients receiving an active comparator (P<0.001)
References: 1. Data on file. Janssen Biotech, Inc. 2. TREMFYA® (guselkumab) [Prescribing Information]. Horsham, PA: Janssen Biotech, Inc.
Difficult-to-treat patient types: Nail data
VOYAGE 1: Mean percentage improvement from baseline NAPSI (target nail)1*†‡
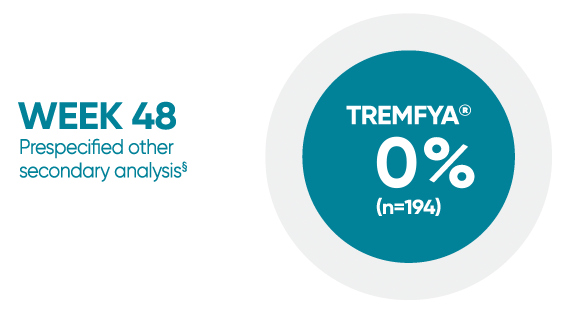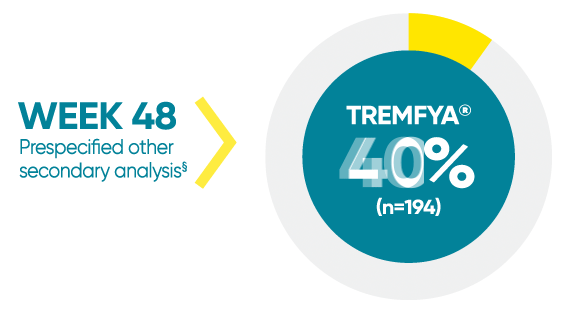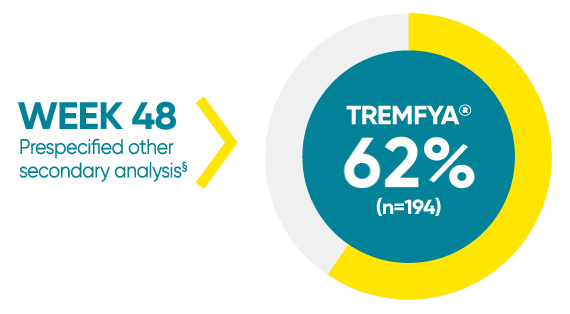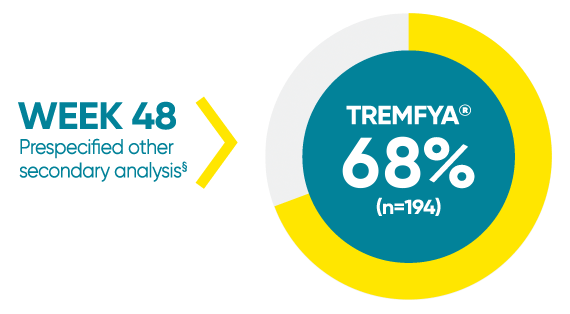
*In a subpopulation of patients with NAPSI (target nail) score >0 at baseline.
‡Limitation: All 10 fingernails may also be evaluated using NAPSI.
§Prespecified other secondary analysis that was not adjusted for multiplicity; therefore, statistical significance has not been established.
VOYAGE co-primary endpoints at Week 16 (NRI)2,3:
VOYAGE 1—PASI 90: TREMFYA® 73% (241/329), placebo 3% (5/174) (P<0.001). IGA 0/1: TREMFYA® 85% (280/329), placebo 7% (12/174) (P<0.001). VOYAGE 2—PASI 90: TREMFYA® 70% (347/496), placebo 2% (6/248) (P<0.001). IGA 0/1: TREMFYA® 84% (417/496), placebo 8% (21/248) (P<0.001).
Psoriasis Symptoms and Signs Diary (Week 16): Greater improvements in symptoms of psoriasis (itch, pain, stinging, burning, and skin tightness).2
Active comparator at Week 48 not shown.
NRI methods were used for analysis.
†Fingernail psoriasis was assessed using NAPSI, in which the nail most affected by psoriasis (target nail) is divided into quadrants and graded for psoriasis of the nail matrix (pitting, leukonychia, red spots in the lunula, and nail plate crumbling) and nail bed (onycholysis, splinter hemorrhages, oil drop discoloration, and nail bed hyperkeratosis) on a scale of 0 to 4 for a total score ranging from 0 to 8; a higher score indicates more severe disease.
NAPSI=Nail Psoriasis Severity Index.
References: 1. Blauvelt A, Papp KA, Griffiths CEM, et al. Efficacy and safety of guselkumab, an anti-interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody, compared with adalimumab for the continuous treatment of patients with moderate to severe psoriasis: results from the phase III, double-blinded, placebo- and active comparator-controlled VOYAGE 1 trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76(3):405-417. 2. TREMFYA® (guselkumab) [Prescribing Information]. Horsham, PA: Janssen Biotech, Inc. 3. Data on file. Janssen Biotech, Inc.
Difficult-to-treat patient types: Palms/soles data
VOYAGE 1: hf–PGA 0/1 and ≥2-grade improvement from baseline1*
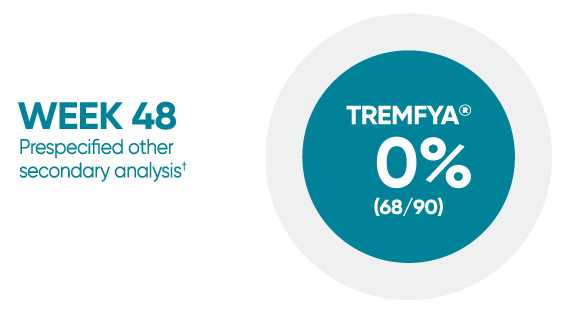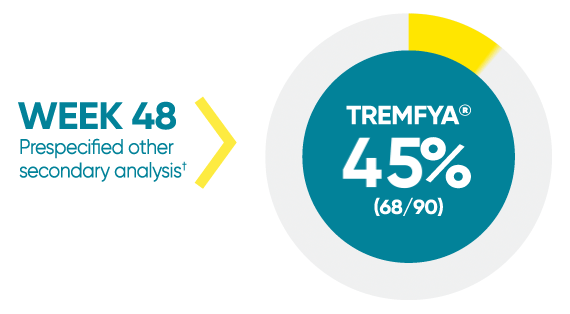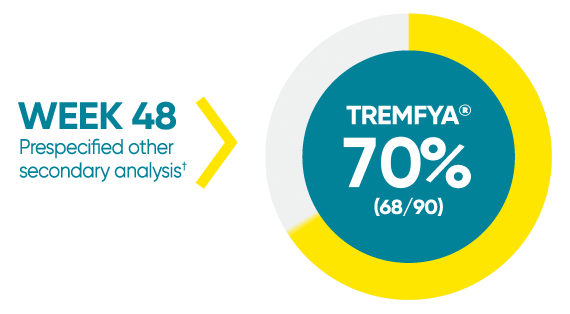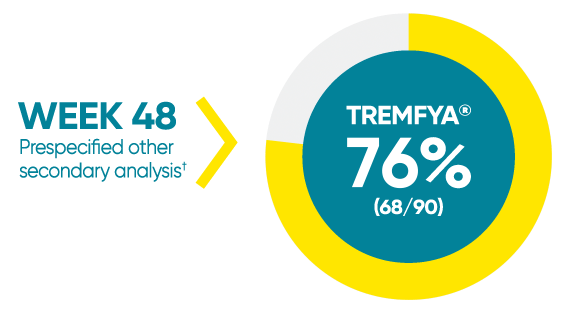
*In a subpopulation of patients with hf-PGA score ≥2 at baseline.
†Prespecified other secondary analysis that was not adjusted for multiplicity; therefore, statistical significance has not been established.
VOYAGE co-primary endpoints at Week 16 (NRI)2,3:
VOYAGE 1—PASI 90: TREMFYA® 73% (241/329), placebo 3% (5/174) (P<0.001). IGA 0/1: TREMFYA® 85% (280/329), placebo 7% (12/174) (P<0.001). VOYAGE 2—PASI 90: TREMFYA® 70% (347/496), placebo 2% (6/248) (P<0.001). IGA 0/1: TREMFYA® 84% (417/496), placebo 8% (21/248) (P<0.001).
Psoriasis Symptoms and Signs Diary (Week 16): Greater improvements in symptoms of psoriasis (itch, pain, stinging, burning, and skin tightness).2
Active comparator at Week 48 not shown.
Nonresponder imputation (NRI) methods were used for analysis.
hf-PGA=Physician's Global Assessment of hands and/or feet; hf-PGA 0/1=patients who achieved hf-PGA score of clear (0); or almost clear (1) using a 5-point scale based on the category that best describes the severity of psoriasis on the palms and soles on a scale of 0 to 4: clear, postinflammatory hyperpigmentation may be present (0), almost clear (1), mild (2), moderate (3), or severe (4).
References: 1. Blauvelt A, Papp KA, Griffiths CEM, et al. Efficacy and safety of guselkumab, an anti-interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody, compared with adalimumab for the continuous treatment of patients with moderate to severe psoriasis: results from the phase III, double-blinded, placebo- and active comparator-controlled VOYAGE 1 trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76(3):405-417. 2. TREMFYA® (guselkumab) [Prescribing Information]. Horsham, PA: Janssen Biotech, Inc. 3. Data on file. Janssen Biotech, Inc.
IN ADULT PATIENTS WITH MODERATE TO SEVERE PLAQUE PsO


